The Challenges of Import Dependence in Pakistan's Economy
Introduction: Import Dependence Burden:
The problem of import dependence has been a long pressing issue in Pakistan's economy, affecting its development. The country's reliance on importing prime goods such as raw materials, machinery and fuel puts the country at risks such as global price volatility. The dependence is further compounded by constant trade deficit which strains the country's foreign exchange reserves and local currency. Addressing the problem of import dependence requires a comprehensive policy framework, along with promoting domestic production to establish economic sustainability and development.
Sectors impacted by Import Dependence:
Some major sectors in Pakistan are highly sensitive to import dependence. For example, the energy sector is highly vulnerable to global oil price volatility, due to its dependence on imported fuel. Similarly, the industrial and agricultural sectors rely on imports of machinery and fertilizers which makes production expensive and constraints competitiveness. This exacerbated dependence negates the growth of domestic manufacturers and diminishes the level of self-sufficiency. It is essential for the country to strengthen such sectors through domestic manufacturing policies which would help in reducing dependence, along with fostering the growth of local industries.
Consequences of Import Dependency on Economy:
The economy of Pakistan is highly affected because of its dependence on import. The trade deficit increases due to increase in import costs compared to export revenue, resulting in depreciation of currency and exhausting foreign exchange reserves. This leads to inflationary consequences, as buying power decreases due to increase in cost of imported goods. Moreover, high reliance on imports supresses local production growth and their confidence. It is essential to address the issue of reliance on imports and boost domestic manufacturing to ensure economic stability in Pakistan, in the long run.
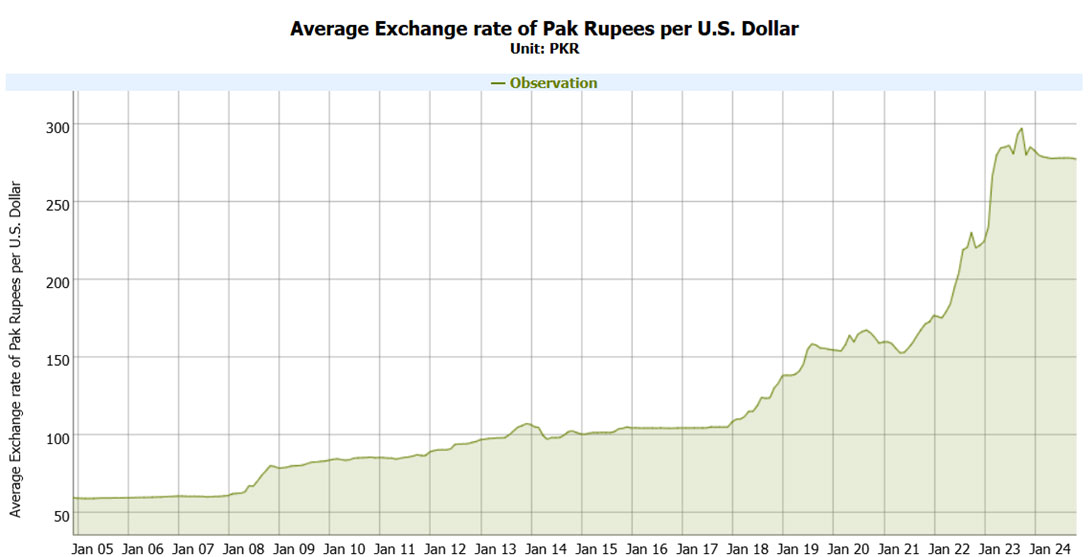
Exchange Rate Volatility and Its Impact on Imports:
The exchange rate is sensitive in Pakistan, which raises the country's import bill. A falling rate of rupee dials up the trade deficit since the costs of imported goods rise. On the other hand, though an appreciating rupee term makes imports cheaper, it might not be good news for most domestic industries. This instability has adverse impacts on business planning for many years ahead because it triggers uncertainties in investments and hence, economic instability. From the Figure 1 below it is clear that the Pakistani Rupee has been depreciating against the US Dollar. This devaluation in currency makes imports more expensive leading to a higher trade deficit possibly contributing towards inflation. The high volatility of the exchange rate is an issue because it provides uncertainty for the companies and interconnects with long-term strategic management and investment planning.
| Figure 1: Nominal Pakistani Rupee to US Dollar Exchange Rate (Source: EasyData, SBP) |
|
Struggles of Domestic Industries under Import Pressure:
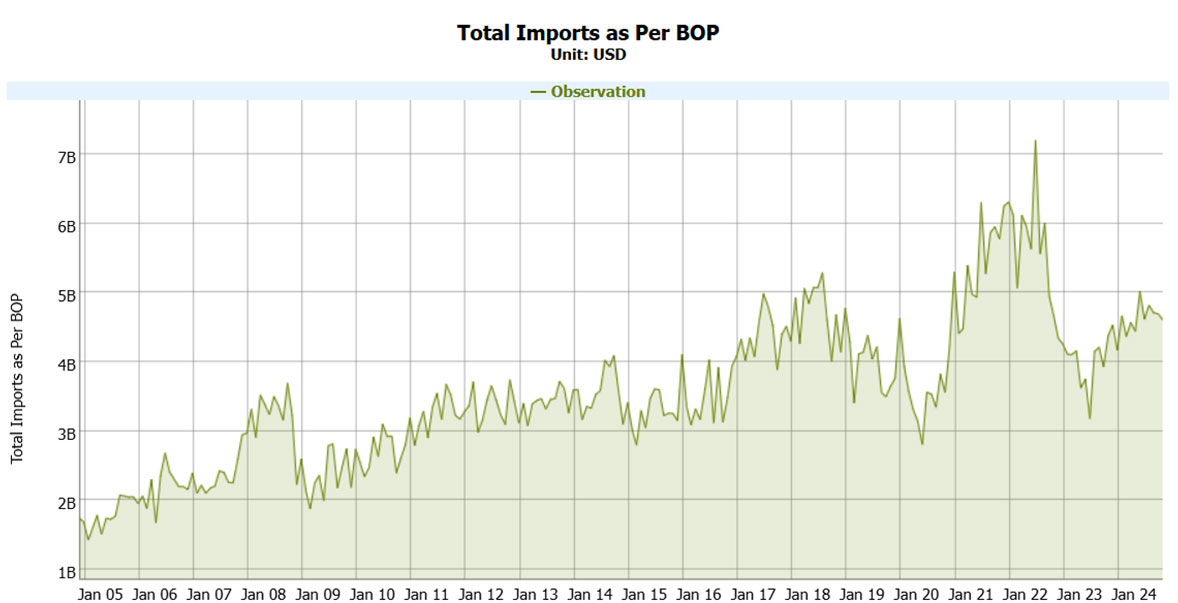
Pakistani domestic industries are struggling due to inexpensive imported goods as presented in the rising import trend in the figure below. This situation means that they have to focus on quality improvement, technological advancement and market diversification in order to survive. They require government support through granting of Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers, subsidies and development of great infrastructure to enhance their competitiveness. Due to this, Pakistan may be able to defend its domestic industries and look for long-term development for the economy.
| Figure 2: Total Imports (Source: EasyData, SBP) |
|
Global Supply Chains and Pakistan's Vulnerabilities:
Pakistan's reliance on imported intermediate goods and raw materials makes it vulnerable to global supply chain disruptions. Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the risks associated with overdependence on foreign suppliers. To mitigate these vulnerabilities, Pakistan needs to diversify its supply chains, promote local manufacturing, and invest in logistics infrastructure to improve the efficiency of domestic production and distribution.
Policy Challenges in Addressing Import Dependence:
At present Pakistan is faced by significant policy challenges in reducing its reliance on imports. The nation's over-reliance on machinery and energy imports result in a persistent trade deficit as the domestic industries are unable to cater these needs. In the short-term policy makers have to tackle issues such as securing foreign exchange reserves while in the longer run industrial development remains a key objective. Often at times, high tariffs and other trade barriers discourage foreign direct investments and pose as a major hindrance in technological advancement. In order to ensure policy consistency, cohesive planning, overcoming institutional weaknesses and defragmentation of the governance is necessary. Policy makers need to introduce export incentives which can help reduce the trade deficit and make the country less vulnerable to external shocks.
Fostering Local Production and Self-Reliance:
Reducing the dependence on imports requires a large-scale push towards local production and self-reliance. Investments in key sectors such as textile, technology and agriculture, while encouraging small and medium enterprises through easier credit access and infrastructural modernization, are a few steps that can be taken in efforts towards greater self-reliance. Over dependence on energy imports by the nation which frequently finds itself grappling with a major power crisis has always been one of the most significant challenges. Expensive energy imports not only take a major hit on the trade balance but also render many industries out of production due to the power crisis. To tackle this challenge, Pakistan should invest on the local production of renewable energy alternatives. Therefore, targeted investments and addressing of the existing structural issues can be a step in the right direction.
Conclusion – A Path Towards Sustainable Economic Growth:
For Pakistan to embark upon the path of sustainable economic growth, it is critical to reduce the dependence on imports. Policymakers need to devise a comprehensive strategy targeting the major shortcomings which have hampered local production and the export potential of the nation. This requires a robust industrial policy, investments in local production along with research and development. The policies devised must consider the nation's strengths in the form of its young labour force and agricultural potential so that sectors with potential for greatest returns can be prioritized. By encouraging domestic resilience and implementation of effective and consistent policies, the nation can pave its path towards economic sustainability and self-reliance. The recent launch of URAAN Pakistan for export-led growth has hope for a turn around; however, its success would once again depend upon how seriously the current Government moves on with its implementation, and how this plan is taken forward through successive Government's ensuring policy consistency.
EGF Blogs
© Institute of Business Administration (IBA) Karachi. All Rights Reserved.